Welcome in the Nick-Lab
 |
Molecular Cell Biology (Prof. Dr. Peter Nick)Fritz-Haber-Weg, Gbd. 30.43 (Biology Tower), 5. floor. e-mail. How to find us Living is Searching (Springer-Nature 2023) Secretary
|
the journal with the longest tradition in cell biology (Springer-Nature). We publish it. more...
|
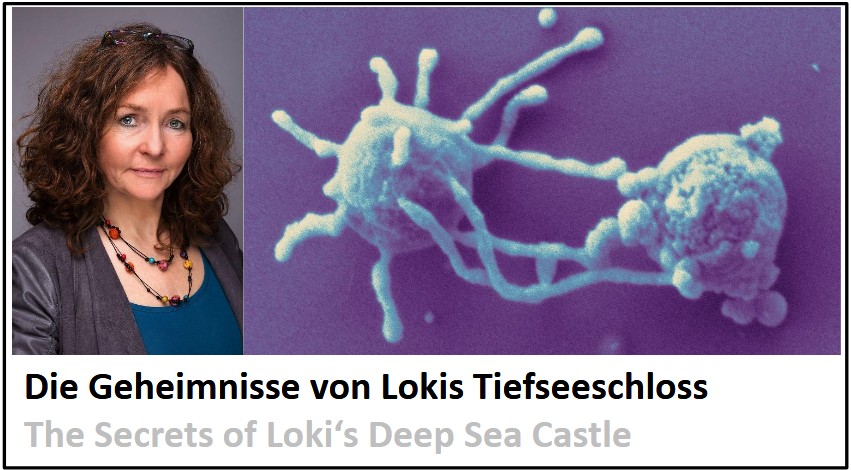 |
The Secrets of Loki's Deep Sea CastleIn frame of the Forum for Critical Interdisciplinarity (more...) we address this semester a central concept of biology - the cell. There is no Life without cells, but what is a cell?
Prof. Dr. Christa Schleper, Universität Wien: Asgard Archaea: the cradle of complex cells.
Di, 09. Dezember 2025, 14:00. Gbd. 40.50 Engler-Bunte HS
The first life forms are thought to have arisen in the deep sea, probably in so-called white smokers, hot springs, where, due to geochemical events, tiny cells from pyrit, but also metallic surfaces, were formed. Microbes without a nucleus conquered our planet later and have remained extremely successful. At one point, however, the modern cells with their uncomparably higher complexity must have been derived. Also we belong to this group of so-called eukaryotes. How this transition might have looked like, had been a mystery for a long time. Only a few years ago, in the depth of the sea between Iceland and Spitzbergen, in a black smoker called Loki's Castle, DNA of such transitional forms had been discovered. In addition to genes typical for anuclear organisms, there were also genes, so far known only from eukaryotes. The organism itself had not been seen by anyone, though. In the meantime it became possible to cultivate a representative of this group, Lokiarchaeum ossiferum, in the laboratory. This makes it possible, for the first time, to investigate the cellular innovations that enabled complex cells.
|
|
 |
Salt Tolerant Sorghum MilletClimate changes makes sea levels rise making fertile coastal land salty. The Nile delta, Bangladesh, Vietnam, but also the South of Italy are already today confronted with salt stress. Can we find crop plants that are able to thrive on such soils? In the past, we have, initiated by our Syrian colleague Dr. Adnan Kanbar, focused on stress resilience in Sorghum Millet. This ancient crop originates from Sudan and can cope with harsh conditions. In fact, we were able to show that some Sorghum varieties not only can grow under salinity, but accumulate more sugar when confronted with salinity. What happens to this sugar, differs - some Sorghum varieties store it in the shoot, what is interesting for bio-economic use (for instance for the production of bio-ethanol) others store it in their seeds, what supports food security in regions affected by soil salinity. During her PhD our colleague Eman Abuslima from Egypt was able to uncover the reason for the different sugar use: a gene switch for the sugar transporter SWEET13 decides. A very active version of this switch could be identified in the old Syrian landrace Razinieh. By breeding, this switch can now be crossed into other millet varieties, and by means of the molecular knowledge, the promising individuals in the progeny can be recognised already in the seedling stage by a simple PCR. Publication 216. Abuslima E, Kanbar A, Ismail A, Raorane ML, Eiche E, El-Sharkawy I, Junker BH, Riemann M, Nick P (2025) Salt stress-induced remodeling of sugar transport: a role for promoter alleles of SWEET13. Nature Sci Rep 15, 7580 - pdf Media echo vbio - idw online - openpress - DBG - pugnalom - Ruhrcampus online |
|
|
|
The new "Strasburger"127 years ago Eduard Strasburger founded the textbook of botany, which appeared now in the 38. edition - this makes the "Strasburger" the biology textbook with the longest history. Peter Nick contributed a couple of 100 pages to the topics structure and function of the plant body and plant development. The "Strasburger" pursues the goal to depict the entire knowledge on plants, comprehensively, up-to-date, and at the same time filtered. Even though it had never been easier to acquire information, the problem is progressively to filter relevant from irrelevant. Textbooks are, therefore, not outdated, but more important than ever. more... |
FKIThe State Teaching Award 2015 was given to Peter Nick and Mathias Gutmann. The money was used to found the Forum. Beyond faculties and disciplines, we debate here on controversial topics. In the WS 2025-2026 we look at a central concept of biology, the cell. more...
ARTTI Podcast on Gene Technology in Agriculture. more...
|
|
|
Microtubules and the Dogs of HellCerberus, the three-headed Dog of Hell guards in Greek mythology the realm of dead, Hades. Herkules succeeds in putting the dog on a leash and by this to intrude into the other world. This metaphor seems to work also for plant immunity: during the so-called Hypersensitive Response the infected cell comits harakiri and by this pulls the attacker into death. This cellular suicide is executed by so-called metacaspases, protein degrading enzymes that by name, but not by evolutionary origin, derive from the caspases that do a similar job during the apoptosis of animal cells. But how does the cell prevent that these Dogs of Hell do not start their destructive work in healthy cells? We have addressed this question in cells of grapevine and found out that the central metacaspase 5 is bound to microtubules, a main component of the plant cytoskeleton. When the cell is sensing an attack (we mimic this in the experiment with chemical signals), it actively makes microtubules disappear and by this releases Cerberus from the leash, who, within a few hours, does a thorough job. Using a combination of cell biological and biochemical approaches we demonstrate this novel, hitherto unknown function of microtubules. Publication 222. Zhu X, Zhang K, Gong P, Riemann M, Nick P (2025) Unleash the Dogs of Death: Vitis Metacaspase 5, Microtubules, and Hypersensitive Response. Plant Cell Reports, doi 10.1007/s00299-025-03567-x - pdf
|
|
 |
EUCOR Project Roots of ResilienceEUCOR, the trinational assocation of Upper-Rhine universities (Karlsruhe, Strasbourg, Freiburg, Colmar-Mulhouse, Basel) launched a call for so-called Seed Money projects. Here, partner KIT-JKIP (Islam Khattab, Peter Nick) together with the University of Basel (Pascale Flury) and the Université Haute-Alsace (Julie Chong) was successful with the project Roots of Resilience. The project tries to render grapevine more resilient against climate-change born novel fungal diseases ("Esca & Co") through improved microbial communities in the rhizosphere. The project is based on results of Kliwiresse, but also previous Upper Rhine Interreg projects, especially Vitifutur and DialogProTec. However, the central reason for the success of the proposal was the cooperation cultivated over four Interreg Upper Rhine networks. The Seed Project in turn will feed into the planned sequel project Robin Root. Planned start is February 2025, running time is two years. more... |
|
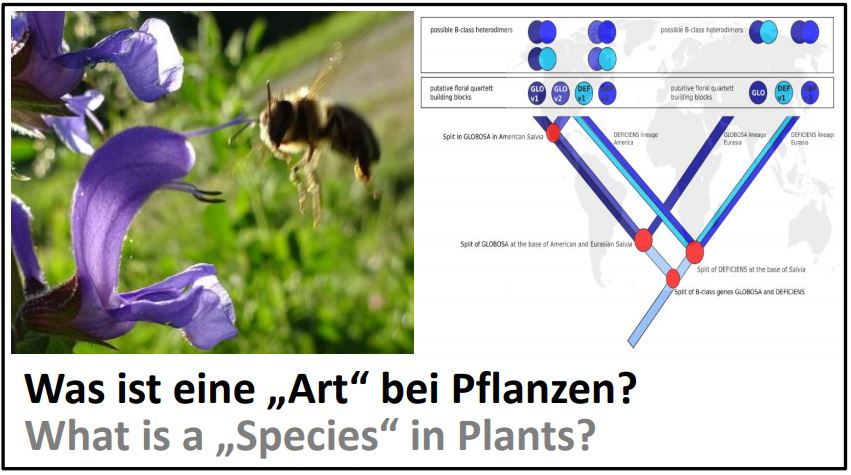 |
EvoDevo of Speciation"Species" are a central concept of biology and usually understood as unit of propagation. This species concept works neatly for animals, because mating of individuals from different species usually do not work or lead to sterile progeny (a classic example would be the mule). Plants, however, do not choose their mating partner themselves, but use insects for doing so. Moreover, plants can circumvent problems with sexuality by asexual propagation. What does "species" now mean for plants? Dr. Sascha Wetters proposed here a new concept, whereby genes that control shape or geometry of flowers are drivers of speciation. To test this idea, he cracked a hard nut - the genus Sage, with more than 1000 known species, one of the most diverse genera at all. Here, he can show that a duplication of the gene switch GLOBOSA facilitated the colonisation of the New World by larger and less asymmetric flowers that recruited novel pollinators, hummingbirds, leading to the birth of numerous new species. This allows to bridge developmental biology and evolution. This work has now been published. 217. Wetters S, Nick P (2025) B-class gene GLOBOSA – a facilitator for enriched species diversity of Salvia in the New World? Plant Biol, 10.1111/plb.70002 - pdf |
|
What our research is about
 |
Evolution solves problems in a sustainable, highly diverse manner. Can we valorise this diversity? We work to protect and use diversity. We develop methods, to safeguard consumer protections in times of globalisation. more... |  |
Our research network, funded by Interreg Upper Rhine uses resilience factors from the almost extinct European Wild Grapevine to develop KliWi-varieties (for Klima-Widerstandsfähig). more... |
 |
Plants are masters of adaptation. How do they overcome stress? We work on jasmonic acid, the plant "adrenalin", but also about the immune system of grapevine. more.. | 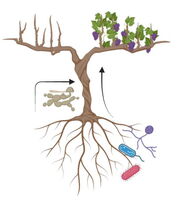 |
Together with partners in Colmar and Basel we try, in the project "Roots of Resilience" to stimulate grapevine immunity by root microbes we have identified in our previous research. more... |
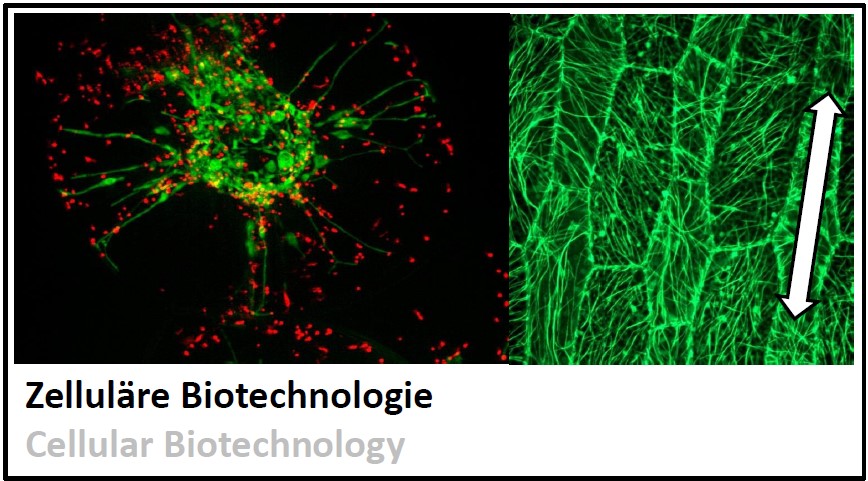 |
Plant cells can self organise without a "Big Brother". Central is the ability of each cell to develop a direction. How does this work? more... | 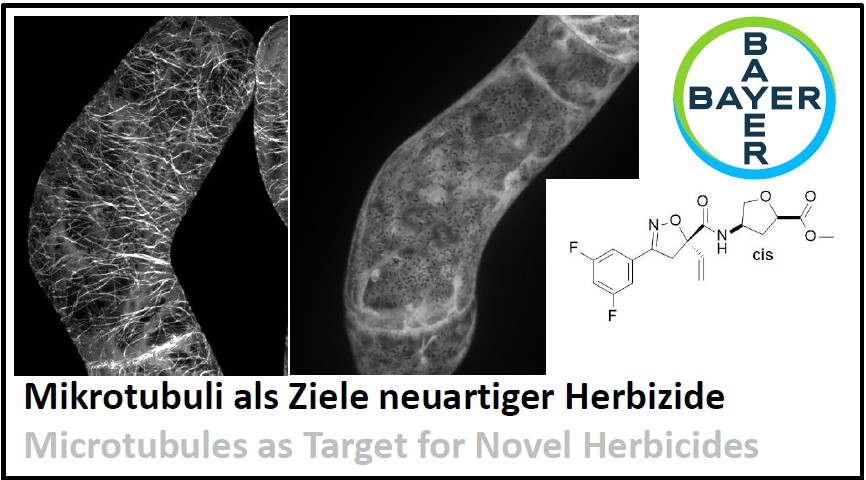 |
Microtubules, a central element of the plant cytoskeleton, steer plant growth. Can we use this to develop less harmful herbicides?(BAYER, 2018-2024) |